Archive for August, 2019
2017 Zika Outbreak in Cuba: 1,384 cases reported by Cuban officials that year. Who knew?
Monday, August 26th, 2019“…….Because most cases of Zika go unconfirmed the outbreak actually may have comprised tens of thousands of infections. ……..”
Cell
Russian medics who treated radiation victims after a military explosion in the Arctic had no protection and now fear they were irradiated themselves.
Sunday, August 25th, 2019“……On 14 August Russia’s weather service Rosgidromet revealed that radiation levels had spiked 16 times above normal, in Severodvinsk, a city 47km (29 miles) east of Nyonoksa……”
Six people were injured Saturday when lightning struck a 60-foot pine at the Tour Championship where they were taking cover from rain
Sunday, August 25th, 20198/24/79AD: Mount Vesuvius erupts in southern Italy, devastating the prosperous Roman cities of Pompeii and Herculaneum and killing thousands.
Saturday, August 24th, 20198/24/1992: Hurricane Andrew makes landfall at 4:52 a.m. 25 miles south of Miami.
Saturday, August 24th, 2019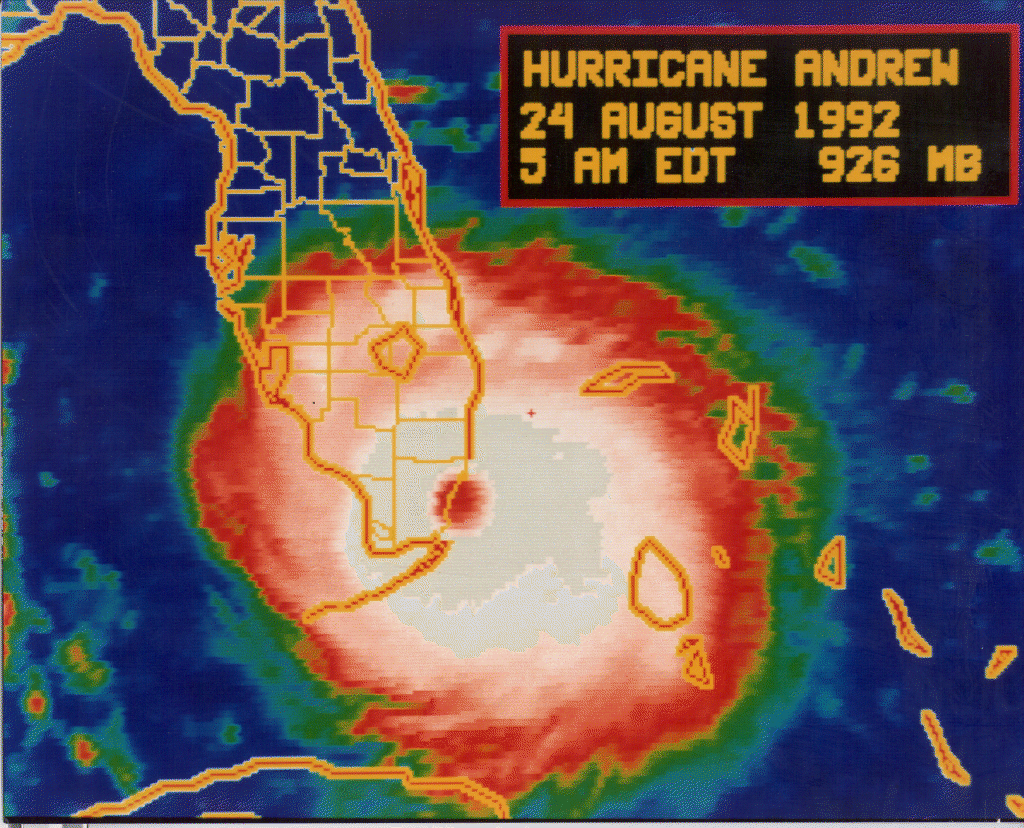
“……Its $47.8 billion worth of devastation no longer ranks it as the most costly natural disaster in American history. But it is probably the most impactful storm to ever hit the U.S.Andrew’s legacy is felt in weather forecasting, building codes and emergency management. When people began crawling out of the debris that morning, they quickly discovered the government was nowhere near prepared…..
Part of the post-disaster disaster was due to complacency. Only two Category 5 hurricanes had ever hit the U.S., and nobody foresaw Andrew turning into a 175-mph monster……
Almost 26,000 homes were totally destroyed, and 102,000 more were damaged. The number of homeless was 160,000, though that didn’t include hundreds of monkeys, snakes, llamas, birds, cougars and other wildlife that escaped from zoos.
Prices for food, batteries, generators and ice soared since there were no laws against gouging. Looters descended and property owners armed themselves to protect what was left of their homes……”
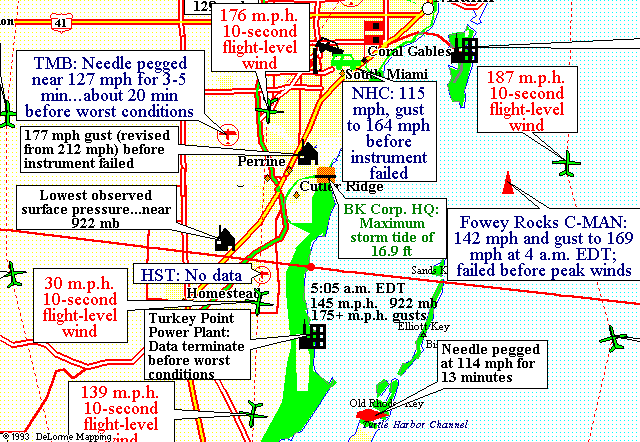
The last radar image taken from NHC before the WSR-57 radar was blown off the roof, 0835 UTC August 24, 1992.
“…During June 2018–March 2019, an outbreak caused by multidrug-resistant Salmonella Newport with decreased susceptibility to azithromycin led to 255 infections and 60 hospitalizations. Infections were linked to Mexican-style soft cheese obtained in Mexico and beef obtained in the United States….”
Saturday, August 24th, 2019Plumb ID, Schwensohn CA, Gieraltowski L, et al. Outbreak of Salmonella Newport Infections with Decreased Susceptibility to Azithromycin Linked to Beef Obtained in the United States and Soft Cheese Obtained in Mexico — United States, 2018–2019. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2019;68:713–717. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm6833a1external icon

Polypills: Good or bad?
Friday, August 23rd, 2019“…….The pill in the study, which involved the participation of 6,800 rural villagers aged 50 to 75 in Iran, contained a cholesterol-lowering statin, two blood-pressure drugs and a low-dose aspirin.
But the study, called PolyIran and published Thursday by The Lancet, was designed 14 years ago……..Its advocates — including some prominent cardiologists — point to the study as evidence that the World Health Organization should endorse distributing such pills without a prescription to hundreds of millions of people over age 50 around the globe. Some have estimated that widespread use could cut cardiac death rates by 60 to 80 percent...….”