Archive for July, 2018
M 6.4 – 5km N of Lelongken, Indonesia: At least 14 dead and over 160 injured.
Sunday, July 29th, 2018The monstrous Carr Fire continues to grow Sunday & 7 persons are still missing
Sunday, July 29th, 20189 people developed botulism type A after eating homemade savory jelly at a private party in Sønderborg, Denmark.
Sunday, July 29th, 2018Synthetic Bioterrorism: New genetic tools are making it easier and cheaper to engineer viruses and bacteria in the lab and potentially making them more contagious and lethal.
Sunday, July 29th, 2018Biodefense in the Age of Synthetic Biology: http://nap.edu/24890
ISBN 978-0-309-46518-2 | DOI 10.17226/24890
Committee on Strategies for Identifying and Addressing Potential Biodefense
Vulnerabilities Posed by Synthetic Biology; Board on Chemical Sciences and
Technology; Board on Life Sciences; Division on Earth and Life Studies;
National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine
One danger is making existing bacteria or viruses more dangerous by giving them antibiotic resistance or altering them so that they produce toxins or evade vaccines.
“…..in a table-top exercise conducted last month by the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security…..experts in pandemic response and national security grappled with a fictional virus called “Clade X” that was created by a terrorist group that inserted genetic elements of deadly Nipah virus into a normally-mild human parainfluenza virus.
The terrorist group in this scenario wanted to depopulate the Earth, and deliberately released the contagious virus at multiple spots around the globe. The resulting pandemic killed 150 million people within a year as officials struggled to contain the social and economic chaos until a vaccine could be made…….”
Heavy Rain And Flash Flooding Threat To Continue In The Northeast; Dangerous Heat In The Western U.S.
Thursday, July 26th, 2018



Greece: The Greek Fire Brigade said the death toll is up to at least 80 people
Thursday, July 26th, 2018The shifting and enduring threat from Islamic extremism around the world that will last long after ISIS is defeated on the battlefield.
Thursday, July 26th, 2018-
From the scheming of lone extremists with no apparent connections to terrorist groups, like the ricin plots, to fighters aligned with the Islamic State or Al Qaeda in more than two dozen countries, terrorist threats are as complex and diverse as ever
-
The Islamic State, in particular, is adapting to setbacks and increasingly using the tools of globalization — including Bitcoin and encrypted communications — to take their fight underground and rally adherents around the world.
-
French authorities foiled a ricin plot by an Egyptian-born student in May after intercepting messages on the secure social media platform Telegram.
-
In Cologne, Germany, authorities acting on information from American intelligence agencies last month arrested a Tunisian man who tried to buy 1,000 castor bean seeds and a coffee grinder online.
“…Tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) cases have significantly increased in 2018, and areas of high risk continue to expand. The Swiss government is considering issuing a nationwide vaccination recommendation against the virus. …”
Thursday, July 26th, 2018“…..Almost 230 people have already been infected with the virus – which in rare cases can be fatal – since the beginning of 2018….
Cases have almost doubled compared to last year’s figures for the same time period…..”

“…..In Switzerland, the tick season starts in March and ends in June, depending on the weather. The health office says ticks are found above all in deciduous forests with lush undergrowth and at an altitude of up to 1,500 metres.
TBE-infected ticks can cause the outbreak of two stages of the disease. During a first episode, which occurs seven to 14 days after the sting, patients suffer flu-like symptoms such as headaches, fever, fatigue or joint complaints.
In 5%-15% of those affected, a second stage of the illness develops, which can last for months and may involve symptoms of meningitis or encephalitis. These symptoms can cause paralysis and leave permanent disabilities. About 1% of cases are fatal….”
Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in China, 2011–17
Thursday, July 26th, 2018“…..Between April 1, 2011, and Oct 31, 2017, 2096 patients with laboratory-confirmed SFTS were admitted. Mean age at admission was 61·4 years (SD 12·2) and 1239 (59%) patients were female. The case fatality rate (CFR) was 16·2% (95% CI 14·6–17·8). A higher risk was associated with being male (unadjusted odds ratio [OR] 1·45, 95% CI 1·15–1·83; p=0·002), older age (for a 10-year increase, unadjusted OR 1·82, 95% CI 1·62–2·04; p<0·0001), longer delay in admission (for every extra day taken before admission to hospital, unadjusted OR 1·18, 1·12–1·24; p<0·0001), presence of diarrhoea (adjusted OR 1·44, 1·12–1·87; p=0·005) or dyspnoea (adjusted OR 8·35, 5·97–11·69; p<0·0001), and development of haemorrhagic signs (adjusted OR 2·79, 95% CI 2·18–3·57; p<0·0001) or neurological symptoms (adjusted OR 30·26, 21·39–42·81; p<0·0001). Laboratory variables that were associated with death included abnormal concentrations of lactate dehydrogenase, aspartate aminotransferase, and blood urea nitrogen, and abnormal neutrophil percentage, which together with age and neurological symptoms were combined in the clinical scoring system. A total score of more than 8 was the optimal threshold to predict risk of death for patients who were evaluated within 6 days after symptom onset (area under the curve 0·879, 95% CI 0·855–0·902). For all participants, viraemia was a strong predictor of fatal outcome (all p<0·0001). Ribavirin therapy was effective in reducing CFR from 6·25% (15 of 240 participants) to 1·16% (two of 173 participants), but only in patients with a viral load below 1×106 copies per mL (hazard ratio 9·72, 95% CI 1·30–72·87; p=0·027)……”

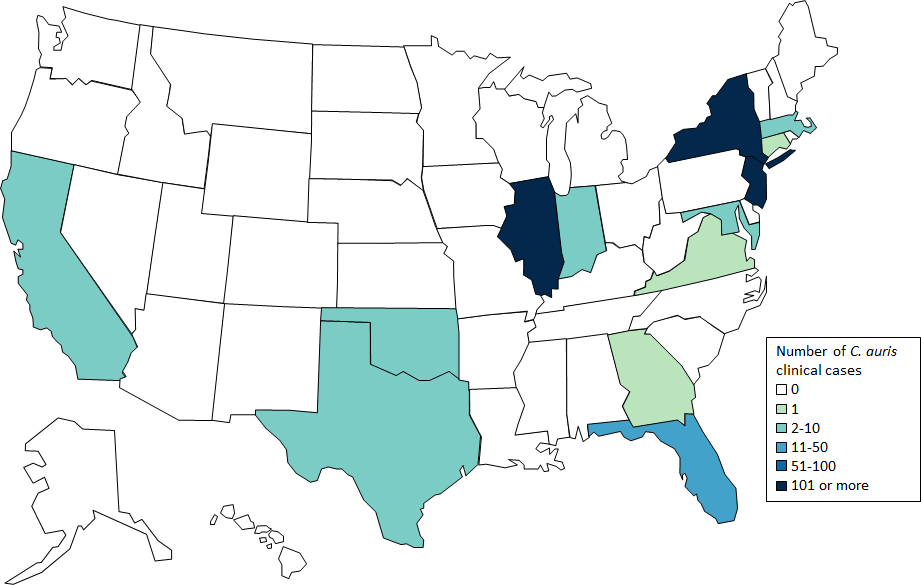
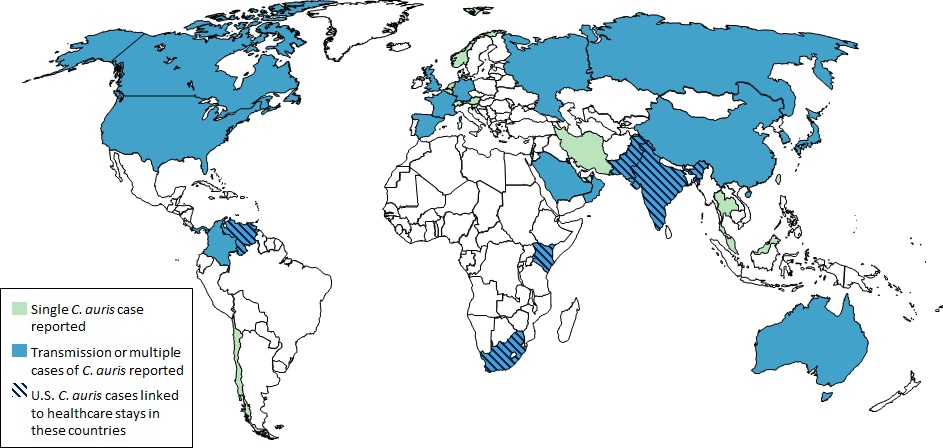
The United States now has 340 confirmed cases of Candida auris
Thursday, July 26th, 2018July 23, 2018: Case Count Updated as of June 30, 2018
Candida auris is an emerging fungus that presents a serious global health threat. C. auris causes severe illness in hospitalized patients in several countries, including the United States. Patients can remain colonized with C. auris for a long time and C. auris can persist on surfaces in healthcare environments. This can result in spread of C. auris between patients in healthcare facilities.
Most C. auris cases in the United States have been detected in the New York City area, New Jersey, and the Chicago area. Strains of C. auris in the United States have been linked to other parts of the world. U.S. C. auris cases are a result of inadvertent introduction into the United States from a patient who recently received healthcare in a country where C. auris has been reported or a result of local spread after such an introduction.