9/21/1938: The Long Island Express, a powerful Category 3 hurricane slams into Long Island and southern New England, causing 600 deaths and devastating coastal cities and towns.
September 21st, 2019New England Hurricane 1938
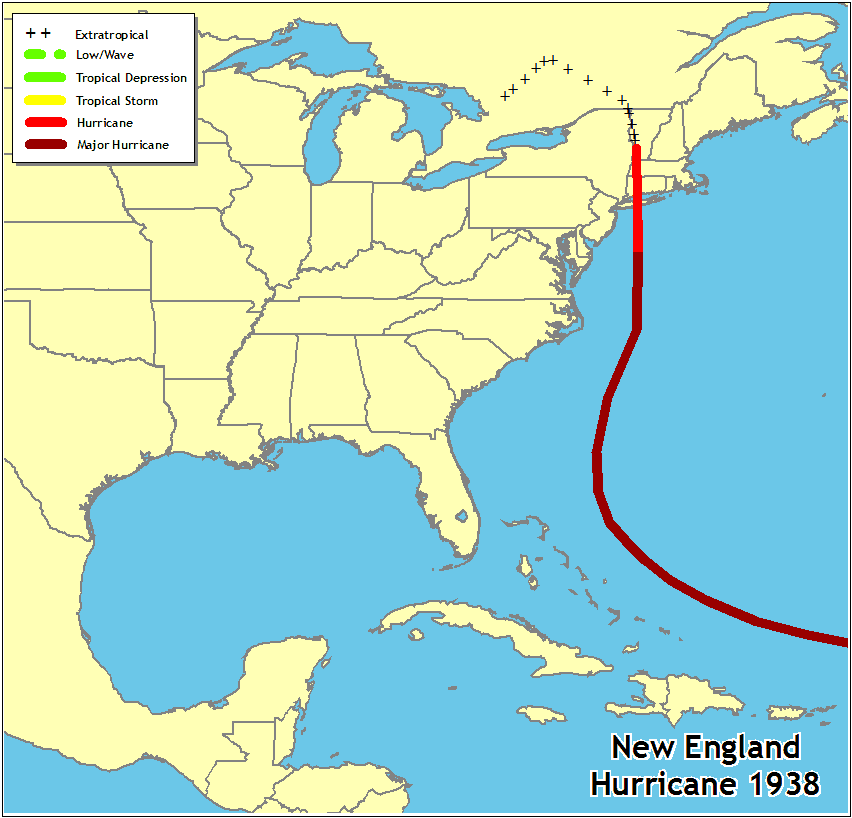
The “Long Island Express” was first detected over the tropical Atlantic on September 13, although it may have formed a few days earlier. Moving generally west-northwestward, it passed to the north of Puerto Rico on the 18th and 19th, likely as a category 5 hurricane. It turned northward on September 20 and by the morning of the 21st it was 100 to 150 miles east of Cape Hatteras, North Carolina. At that point, the hurricane accelerated to a forward motion of 60 to 70 mph, making landfall over Long Island and Connecticut that afternoon as a Category 3 hurricane. The storm became extratropical after landfall and dissipated over southeastern Canada on September 22.
Blue Hill Observatory, Massachusetts measured sustained winds of 121 mph with gusts to 183 mph (likely influenced by terrain). A U.S. Coast Guard station on Long Island measured a minimum pressure of 27.94 in. Storm surges of 10 to 12 ft inundated portions of the coast from Long Island and Connecticut eastward to southeastern Massachusetts, with the most notable surges in Narragansett Bay and Buzzards Bay. Heavy rains before and during the hurricane produced river flooding, most notably along the Connecticut River.
This hurricane struck with little warning and was responsible for 600 deaths and $308 million in damage in the United States.