Archive for March, 2018
Saudi Arabia’s MERS-CoV total cases since 2012 have now reached 1,816, including 736 deaths.
Tuesday, March 20th, 2018
OpenWHO is WHO’s new interactive, web-based, knowledge-transfer platform offering online courses to improve the response to health emergencies.
Monday, March 19th, 2018OpenWHO enables the Organization and its key partners to transfer life-saving knowledge to large numbers of frontline responders.
3/18/1937: Nearly 300 students in Texas are killed by an explosion of natural gas at their school
Sunday, March 18th, 2018“…..The Consolidated School of New London, Texas, sat in the middle of a large oil and natural gas field. The area was dominated by 10,000 oil derricks, 11 of which stood right on school grounds. The school was newly built in the 1930s for close to $1 million and, from its inception, bought natural gas from Union Gas to supply its energy needs. The school’s natural gas bill averaged about $300 a month. Eventually, officials at Consolidated School were persuaded to save money by tapping into the wet-gas lines operated by Parade Oil Company that ran near the school. Wet gas is a type of waste gas that is less stable and has more impurities than typical natural gas…..”
Two new clinical trials testing an experimental vaccine to prevent influenza caused by an H7N9 influenza virus are now enrolling volunteers at sites across the United States.
Sunday, March 18th, 2018‘…..H7N9 is an avian (bird) influenza virus first reported in humans in 2013 in China. Since then, six waves of H7N9 infection have occurred in China, resulting in more than 1,500 cumulative human infections, according to the World Health Organization. No human cases of H7N9 influenza have been detected to date in the United States. Currently, the virus does not spread easily from person to person; rather, people typically become infected through direct exposure to infected poultry or contaminated environments. However, if the virus mutates and becomes easily transmissible between humans, it could result in an influenza pandemic because most people have little to no immunity to it. H7N9 has a high mortality rate, resulting in death in 39 percent of those who became infected.…..’

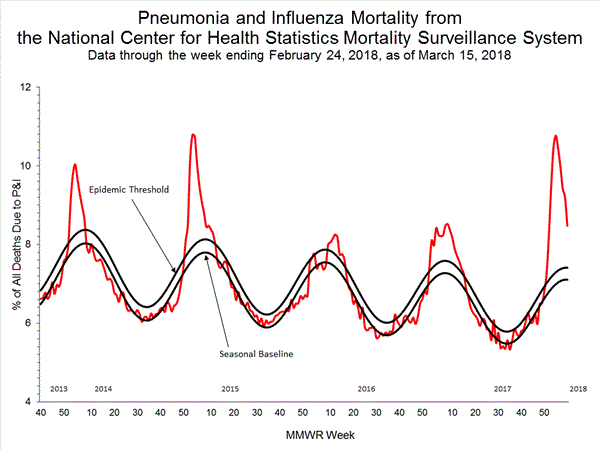
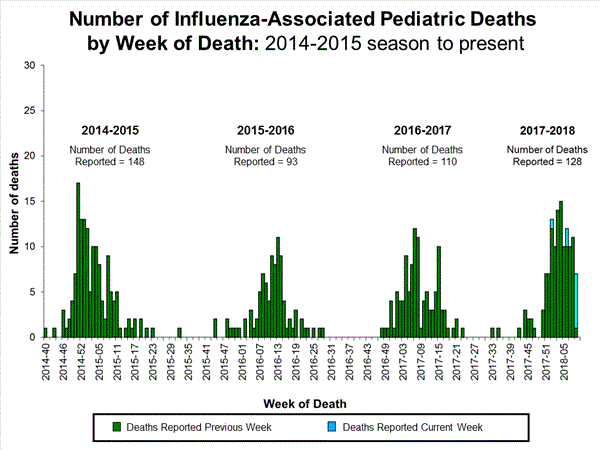
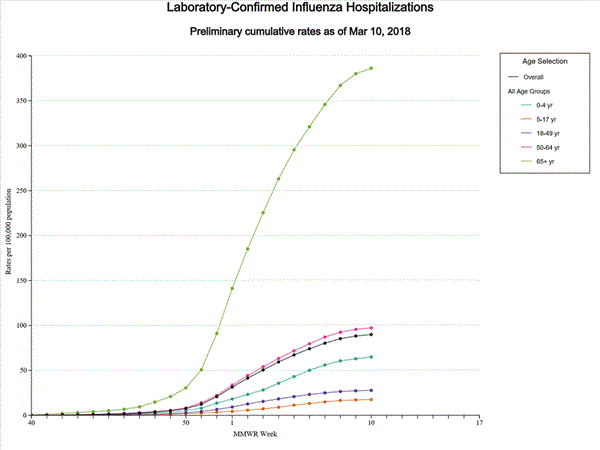
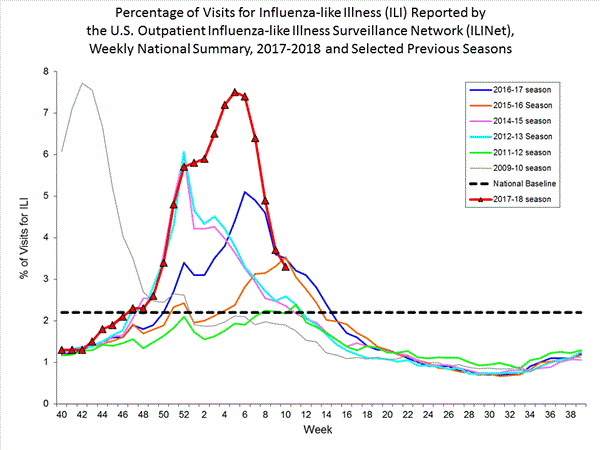
CDC: During week 10 (March 4-10, 2018), influenza activity decreased in the United States.
Sunday, March 18th, 2018Since January 2018, 10 travel-related cases of yellow fever, including four deaths, have been reported in international travelers returning from Brazil.
Sunday, March 18th, 2018Chemical agents: Live, Binary, and Dusty; what’s the difference?
Sunday, March 18th, 2018Binary: Chemical weapons wherein the toxic agent is not in its active state, but rather, the toxin is in the form of chemical precursors that are physically separated within the weapon and combine after deployment to the active state.
A dusty agent is the dried powder form of a poison.
A “live” agent is fully mixed and fully activated once loaded into warheads or bombs.
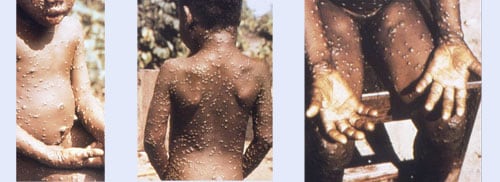
Six African countries have confirmed human cases of monkeypox since 2016, many of which had not reported a case in decades.
Saturday, March 17th, 2018“……What is already known about this topic?
Human monkeypox is a viral zoonosis that occurs in West Africa and Central Africa. Most cases are reported from Democratic Republic of the Congo. The disease causes significant morbidity and mortality, and no specific treatment exists.
What is added by this report?
Nigeria is currently experiencing the largest documented outbreak of human monkeypox in West Africa. During the past decade, more human monkeypox cases have been reported in countries that have not reported disease in several decades. Since 2016, cases have been confirmed in Central African Republic (19 cases), Democratic Republic of the Congo (>1,000 reported per year), Liberia (two), Nigeria (>80), Republic of the Congo (88), and Sierra Leone (one). The reemergence of monkeypox is a global health security concern.
What are the implications for public health practice?
A recent meeting of experts and representatives from affected countries identified challenges and proposed actions to improve response actions and surveillance. The World Health Organization and CDC are developing updated guidance and regional trainings to improve capacity for laboratory-based surveillance, detection, and prevention of monkeypox, improved patient care, and outbreak response……”
A pedestrian bridge suddenly collapsed onto the road below near Florida International University, crushing cars, killing 4 and sending at least 9 to hospitals
Friday, March 16th, 2018Saudi Arabia has spent billions in fighting Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) since 2012.
Friday, March 16th, 2018“…..The ministry has taken a number of precautionary and preventive measures to contain the disease.
More than 3,000 firms have been closed down as part of temporary and permanent punitive measures.
Seven health ministers have worked to eradicate MERS-CoV since it broke out first in the Kingdom. They are Dr. Abdullah Al-Rabeeah (1430-35 Hijri), Adel Fakeih (1435-36 Hijri), Dr. Mohammed Ali Al-Hayazie (1436 Hijri), Ahmed Oqail Al-Khateeb (1436 Hijri), Mohammed Abdulmalik Al-Asheikh (1436 Hijri), Khalid Al-Falih (1436-37 Hijri) and Dr. Tawfiq Al-Rabiah (the present minister)…..”