Archive for December, 2015
PAHO: Cases of chikungunya in the Americas and Caribbean rose by only 1,191 last week, marking the second straight week of low numbers and bringing the outbreak total to 1,790,681.
Tuesday, December 22nd, 2015Zika Virus Outbreaks: Here and There
Tuesday, December 22nd, 2015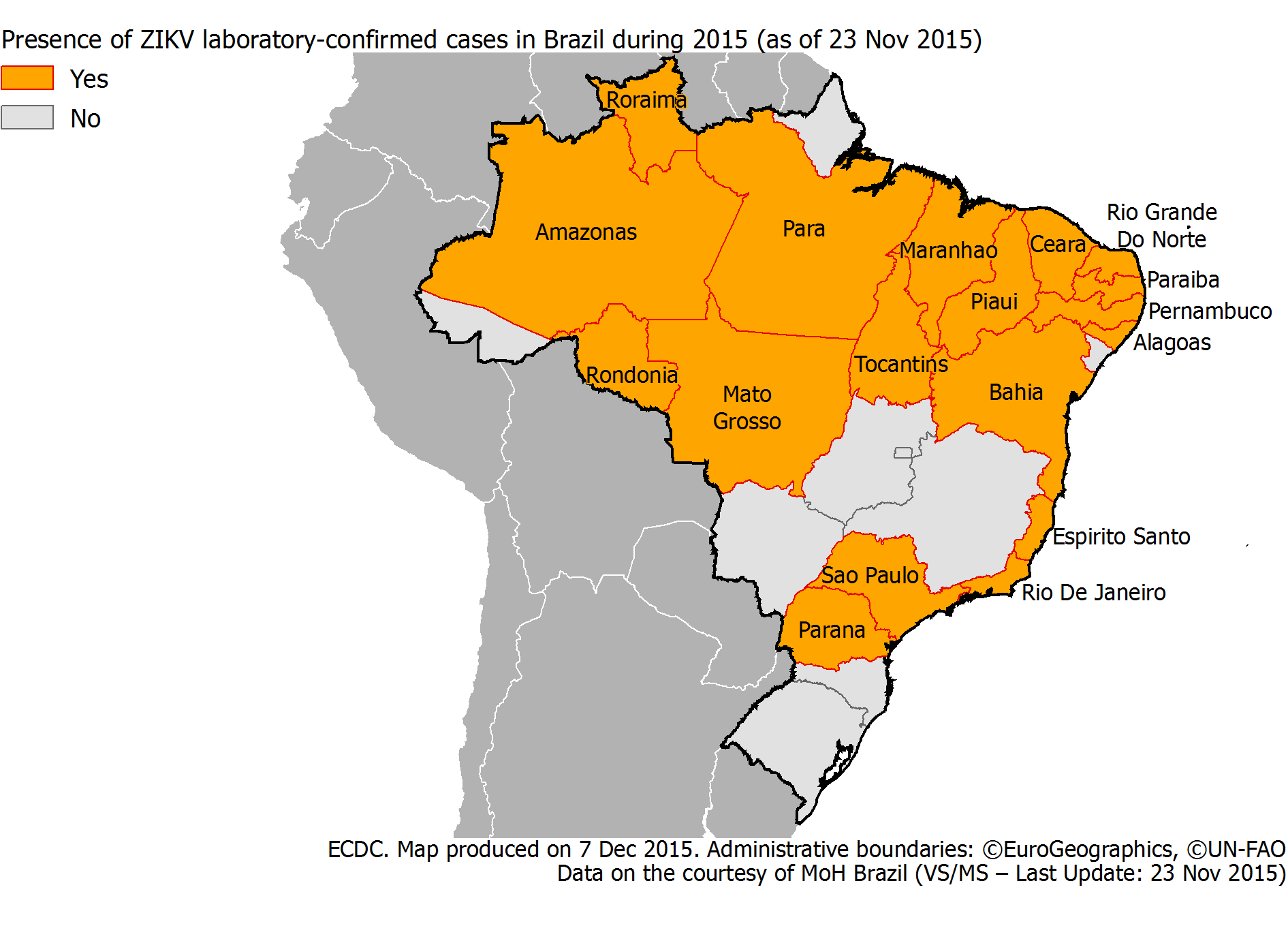
Epidemiological update: Outbreaks of Zika virus and complications potentially linked to the Zika virus infection
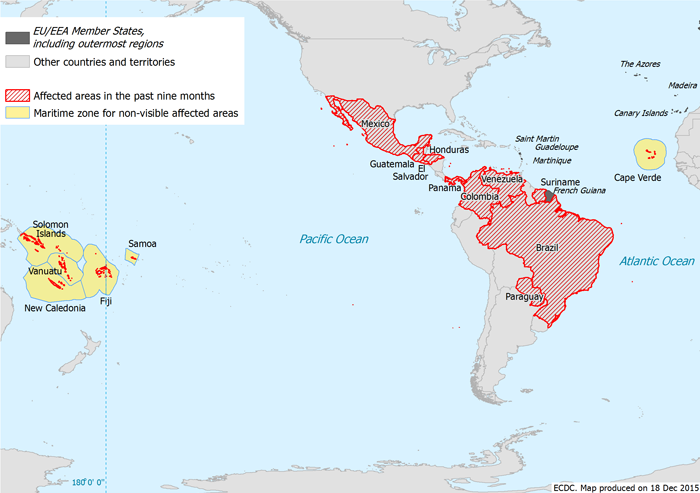
No autochthonous cases of Zika virus infection have been reported in EU Member States so far in 2015. In the past month, one imported case was reported in the Netherlands in a traveller who returned from Suriname on 29 November 2015 after a 3-week holiday in that country.
Autochthonous transmission of Zika virus infection has been reported in Brazil since April 2015. As of week 47/2015, 18 states in Brazil have reported locally-acquired cases [1].
Since the beginning of 2015, sporadic autochthonous cases have been reported in Samoa, Fiji, New Caledonia, the Solomon Islands, and Vanuatu [4]. New Zealand reported two imported cases from Samoa.
On 3 November 2015, the Cape Verdean Ministry of Health reported an outbreak with around 1 000 suspected cases [5]. Seventeen out of 64 blood samples that were sent for confirmation to the Pasteur Institute in Dakar were positive for Zika virus [6].
| Brazilian states | Cases of microcephaly under investigation | Confirmed cases* | Discarded cases* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pernambuco | 874 | 29 | 17 |
| Paraíba | 322 | 19 | 30 |
| Bahia | 316 | 0 | 0 |
| Alagoas | 107 | 0 | 0 |
| Rio Grande do Norte | 101 | 35 | 4 |
| Ceará | 79 | 0 | 0 |
| Mato Grosso | 72 | 0 | 0 |
| Rio de Janeiro | 57 | 0 | 0 |
| Maranhão | 56 | 0 | 7 |
| Tocantins | 43 | 0 | 7 |
| Piauí | 39 | 0 | 0 |
| Minas Gerais | 33 | 0 | 2 |
| Sergipe | 33 | 51 | 34 |
| Espírito Santo | 14 | 0 | 0 |
| São Paulo | 6 | 0 | 0 |
| Goiás | 4 | 0 | 1 |
| Mato Grosso do Sul | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| Pará | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| Distrito Federal | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| Rio Grande do Sul | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 2 165 | 134 | 102 |
References
2. Secretaría de Estado en el Despacho de Salud. Communicado [Internet]. Tegucigalpa: Secretaria de Salud en Honduras; 2015 [cited 2015 Dec 17]. Available from: http://www.salud.gob.hn/.
3. World Health Organization. Disease Outbreak News: Zika virus infection – Suriname [Internet]. Geneva: World Health Organization (WHO); 2015 [updated 2015 Nov 13; cited 2015 Nov 13]. Available from: http://www.who.int/csr/don/13-november-2015-zika/en/.
4. European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Zika virus epidemic in the Americas: potential association with microcephaly and Guillain-Barré syndrome [Internet]. Stockholm: ECDC; 2015 [cited 2015 Dec 10]. Available from: http://ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications/Publications/zika-virus-americas-association-with-microcephaly-rapid-risk-assessment.pdf.
5. ProMED-mail. Zika virus – Suriname, Cape Verde [Internet]. 2015 [cited 2015 Nov 06]. Available from: http://www.promedmail.org/direct.php?id=20151106.3770696.
6. Ministério da Saúde (Capo Verde). Ministério da Saúde confirma infecção por Vírus Zika no concelho da Praia [Internet]. Santiago Island2015 [updated 2015 Nov 2; cited 2015 Nov 2]. Available from: http://www.minsaude.gov.cv/index.php/rss-noticias/912-ministerio-da-saude-confirma-infeccao-por-virus-zika-no-concelho-da-praia.
7. Ministério da Saúde (Brazil). Monitoramento dos casos de Microcefalias no Brasil, até a semana epidemiológica 48, 2015. Boletim Epidemiológico da Secretaria de Vigilância em Saúde. Vol. 46, Nº 41, 2015. [Internet]. 2015. Available from: http://portalsaude.saude.gov.br/images/pdf/2015/dezembro/11/svs-be-2015-048-microcefalia-se48-final2.pdf.
8. Centro de operações de emergências em saúde pública sobre microcefalias. Monitoramento dos casos de microcefalias no brasil informe epidemiológico Nº 04/2015 – semana epidemiológica 49 (06/12 a 12/12/2015) [Internet]. 2015 [cited 2015 Dec 5]. Available from: http://portalsaude.saude.gov.br/images/pdf/2015/dezembro/15/COES-Microcefalias—Informe-Epidemiol–gico—SE-49—15dez2015—10h.pdf.
12/21/1988: A terrorist bomb exploded aboard a Pan Am Boeing 747 over Lockerbie, Scotland, killing 270 souls.
Monday, December 21st, 2015Landslide in China: 91 missing;
Monday, December 21st, 2015https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uo61CYqv-oY
China: At least 91 missing one day after a mountain of excavated soil and construction waste buried dozens of buildings when it swept through an industrial park in Shenzhen.
Monday, December 21st, 2015A landslide in the southern Chinese city of Shenzhen results in buildings destroyed and a search for the missing.
Monday, December 21st, 2015** At least 27 people were unaccounted for as of Sunday evening
** 1,500 rescue workers searching amidst the rubble
A fiberglass ferry crossing the Gulf of Bone with 110 passengers and 12 crew was overwhelmed by waves more than 3 meters high during stormy weather on Saturday afternoon. Scores missing, 39 rescued so far.
Sunday, December 20th, 2015** Indonesian boat accidents have killed hundreds of people in recent years.
** Boats are often overcrowded
** Safety regulations are poorly enforced.

CDC- Ebola Response: Year in Review
Sunday, December 20th, 2015Ebola Response: Year in Review
Posted on December 14, 2015 by
Throughout the month of December, Public Health Matters is conducting a series of year-in-review posts of some of the most impactful disease outbreaks of 2015. These posts will give you a glimpse of the work CDC is doing to prevent, identify, and respond to public health threats.
Getting to Zero
Getting to Zero was a theme and goal that dominated much of CDC’s attention in 2015. In January 2015, The World Health Organization reported that the Ebola epidemic had reached a turning point with the most impacted countries, Liberia, Guinea and Sierra Leone, seeing declines in the number of new cases of Ebola. This turning point came after a year of battling the worst Ebola outbreak in history—resulting in over 20,000 cases by December 2014.
While the spread of the disease and U.S. media attention was at its peak in 2014, some of CDC’s most impactful and important work took place in 2015. This year’s response to the Ebola epidemic was marked with many challenges and accomplishments, new discoveries, and continuous hard work by hundreds of CDC staff. The dedication of CDC and its partners throughout the year has also led to the successful end of widespread Ebola transmission in Liberia and Sierra Leone.
Ebola Vaccine Trials
In April 2015, CDC, in partnership with The College of Medicine and Allied Health Sciences, University of Sierra Leone, and the Sierra Leone Ministry of Health and Sanitation, began a clinical trial to test the potential of a new vaccine to protect against the Ebola virus. This vaccine trial, known as Sierra Leone Trial to Introduce a Vaccine against Ebola (STRIVE), is designed to help protect against Zaire ebolavirus, the virus that is causing the current outbreak in West Africa.
 “A safe and effective vaccine would be a very important tool to stop Ebola in the future, and the front-line workers who are volunteering to participate are making a decision that could benefit health care professionals and communities wherever Ebola is a risk,” said CDC Director Tom Frieden, M.D., M.P.H. “We hope this vaccine will be proven effective but in the meantime we must continue doing everything necessary to stop this epidemic —find every case, isolate and treat, safely and respectfully bury the dead, and find every single contact.”
“A safe and effective vaccine would be a very important tool to stop Ebola in the future, and the front-line workers who are volunteering to participate are making a decision that could benefit health care professionals and communities wherever Ebola is a risk,” said CDC Director Tom Frieden, M.D., M.P.H. “We hope this vaccine will be proven effective but in the meantime we must continue doing everything necessary to stop this epidemic —find every case, isolate and treat, safely and respectfully bury the dead, and find every single contact.”
This vaccine trial, along with a series of other vaccine trials taking place in West Africa, represents an important step in the response to the Ebola epidemic. In addition to the tireless efforts being made to completely eliminate Ebola cases, efforts to discover a vaccine could prevent an outbreak of this size in the future.
Leaving Lasting Infrastructures for Health
Programs like STRIVE seek to contribute not only to the future of Ebola prevention research, but also to the future of health care capabilities in the areas impacted by the Ebola epidemic. The STRIVE study is strengthening the existing research capacity of institutions in Sierra Leone by providing training and research experience to hundreds of staff to use now and for future studies.
CDC is leaving behind newly created emergency operation centers (EOC) in countries affected by widespread Ebola outbreaks. The ministries of health will fully lead these new EOCs, which will provide a place to train healthcare workers to be better prepared to conduct outbreak surveillance and response.
Additionally, 2015 brought the official announcement of plans to create the African Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (African CDC). First proposed in 2013, the African CDC will seek ongoing collaboration with other public health entities across the continent and the world to elevate health outcomes for all citizens. Partners will assist by implementing activities, supporting the establishment of regional collaborating centers, advising the African CDC leadership and staff, and providing technical assistance.
Celebrate the Successes, Look to the Future
2015 brought significant progress in the Ebola response. Yet, while the successes and improvements made to public health infrastructure in West Africa are important to celebrate, the work continues to get to zero and end the largest Ebola outbreak in history.
As we draw closer to our goal of zero cases of Ebola, we are reminded of how critical it is to identify, prevent, and respond to outbreaks to prevent future epidemics of this magnitude.
Posted on December 14, 2015 by
‘Meeting at Dabiq’: ISIS’ apocalyptic vision of the end of the world
Sunday, December 20th, 2015https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UwMIHac-lwQ