Multistate Outbreak of Cyclospora Illnesses Likely Linked to Salads from McDonald’s
August 2nd, 2018The FDA confirms the presence of Cyclospora in Fresh Express salad mix through new laboratory method; Fresh Express recalls expired products containing romaine lettuce.
July 31, 2018 Update
The FDA has confirmed the presence of Cyclospora in an expired salad mix, containing romaine lettuce and carrots, that was produced by the processor Fresh Express in Streamwood, Illinois.
On July 26, 2018, the FDA completed final analysis of an unused package of Fresh Express salad mix containing romaine lettuce and carrots, which had been distributed to McDonald’s. The analysis confirmed the presence of Cyclospora in that sample, though the expiration date for that product, July 19, had already passed. On July 27, the FDA informed Fresh Express of the results, and instructed Fresh Express to determine whether potentially contaminated product may still be on the market.
Fresh Express reported to FDA that the romaine from the same lot as the positive sample was not packaged for direct retail sale by Fresh Express and had already expired. Fresh Express committed to using recall procedures to inform companies that received additional products of concern about the sample result. Fresh Express also reported that the carrots in the sampled salad mix only went to McDonald’s.
On July 30, 2018, the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s Food Safety and Inspection Service (FSIS) issued a public health alert on beef, pork and poultry salad and wrap products potentially contaminated with Cyclospora that was distributed by Caito Foods LLC, of Indianapolis, Ind. The products were produced between July 15 and 18, 2018, with either “Best By,” “Enjoy by,” “Best if Sold By” or “Sell By” dates ranging from July 18 through July 23, 2018. Caito Foods had received notification from Fresh Express that the chopped romaine in these products was being recalled.
McDonald’s reports that they stopped using the Fresh Express salad mix at impacted restaurants in IL, IA, IN, WI, MI, OH, MN, NE, SD, MT, ND, KY, WV, and MO on July 13, 2018. The company has since reported that it has replaced the supplier of salads in those states. More information can be found in McDonald’s Statement.
In 2015, FDA set up a multidisciplinary workgroup to prioritize the development, validation and implementation of a method for detecting Cyclospora in fresh produce. In 2018, FDA began using the newly validated Cyclospora method. The availability of this method is a significant advancement in FDA’s ability to investigate outbreaks of cyclosporiasis and identify the parasite in foods.
The investigation is ongoing and the FDA is currently reviewing distribution and supplier information for romaine and carrots.
Fast Facts
- The FDA, CDC, along with state and local officials are investigating a multi-state outbreak of cyclosporiasis illnesses likely linked to salads from McDonald’s restaurants.
- On July 26, 2018, the FDA completed final analysis of an unused package of Fresh Express salad mix containing romaine lettuce and carrots, which had been distributed to McDonald’s. The analysis confirmed the presence of Cyclospora in that sample, though the expiration date for that product, July 19, had already passed. On July 27, the FDA informed Fresh Express of the results.
- FDA instructed Fresh Express to determine whether potentially contaminated product may still be on the market. Fresh Express reported to FDA that the romaine from the same lot as the positive sample was not packaged for direct retail sale by Fresh Express and had already expired. Fresh Express committed to using recall procedures to inform those companies that received this romaine about the sample result. Fresh Express also reported that carrots used in the mix were only sent to McDonald’s locations.
- On July 30, 2018, the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s Food Safety and Inspection Service (FSIS) issued a public health alert on beef, pork and poultry salad and wrap products potentially contaminated with Cyclospora that were distributed by Caito Foods LLC, of Indianapolis, IN. The products were produced between July 15 and 18, 2018, with either “Best By,” “Enjoy by,” “Best if Sold By” or “Sell By” dates ranging from July 18 through July 23, 2018. Caito Foods had received notification from Fresh Express that the chopped romaine in these products was being recalled.
- The CDC reports that 286 people in 15 states have become ill. There have been 11 hospitalizations and no deaths.
- The investigation is ongoing and the FDA is currently reviewing distribution and supplier information for romaine and carrots.
- As of July 13, 2018, McDonald’s decided to voluntarily stop selling salads at impacted restaurants in IL, IA, IN, WI, MI, OH, MN, NE, SD, MT, ND, KY, WV, and MO. The company has since reported that it has replaced the supplier of salads in those states. More information can be found in McDonald’s Statement.
- Consumers who have symptoms of cyclosporiasis should contact their health care provider to report their symptoms and receive care. Most people infected with Cyclospora develop diarrhea, with frequent, sometimes explosive, bowel movements. Other common symptoms include loss of appetite, weight loss, stomach cramps/pain, bloating, increased gas, nausea, and fatigue. Vomiting, body aches, headache, fever, and other flu-like symptoms may be noted. Some people who are infected with Cyclospora do not have any symptoms. If not treated, the illness may last from a few days to a month or longer. Symptoms may seem to go away and then return one or more times (relapse).
- At this time, we do not have evidence to suggest that this cluster of illnesses is related to the ongoing Cyclospora outbreak linked to Del Monte vegetable trays.
What is the Problem and What is Being Done About It?
FDA, CDC, state, and local partners are currently investigating several Cyclospora illnesses associated with McDonald’s locations in IA, IL, IN, KY, MN, MO, NE, OH, SD, and WI.
CDC has reported 286 laboratory-confirmed cases of cyclosporiasis in persons from CT, FL, IA, IL, IN, KY, MI, MN, MO, NE, OH, SD, TN, VA and WI who reportedly consumed salad products from several McDonald’s locations. The Florida case-patient purchased a salad while traveling in Kentucky and the Connecticut, Michigan, Tennessee, and Virginia case-patients purchased salads while traveling in Illinois.
On July 26, 2018, the FDA completed final analysis of an unused package of Fresh Express salad mix containing romaine lettuce and carrots, which had been distributed to McDonald’s. The analysis confirmed the presence of Cyclospora in that sample, though the expiration date for that product, July 19, had already passed. On July 27, the FDA informed Fresh Express of the results.
Fresh Express reported to FDA that the romaine from the same lot as the positive sample was not packaged for direct retail sale by Fresh Express and had already expired. Fresh Express committed to using recall procedures to inform those companies that received this romaine about the sample result.
On July 30, 2018, the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s Food Safety and Inspection Service (FSIS) issued a public health alert on beef, pork and poultry salad and wrap products potentially contaminated with Cyclospora that were distributed by Caito Foods LLC, of Indianapolis, Ind. The products were produced between July 15 to 18, 2018, with either “Best By,” “Enjoy by,” Best if Sold By” or “Sell By” dates ranging from July 18 through July 23, 2018. Caito Foods had received notification from Fresh Express that the chopped romaine in these products was being recalled.
Fresh Express reported that the carrots in the mix only went to McDonald’s.
McDonald’s reports that they stopped using the Fresh Express salad mix at impacted restaurants in IL, IA, IN, WI, MI, OH, MN, NE, SD, MT, ND, KY, WV, and MO on July 13, 2018. The company has since reported that it has replaced the supplier of salads in those states. More information can be found in McDonald’s Statement.
The investigation is ongoing and the FDA is currently reviewing distribution and supplier information for romaine and carrots.
Consumers who have symptoms of cyclosporiasis should contact their health care provider to report their symptoms and receive care. Most people infected with Cyclospora develop diarrhea, with frequent, sometimes explosive, bowel movements.
Other common symptoms include loss of appetite, weight loss, stomach cramps/pain, bloating, increased gas, nausea, and fatigue. Vomiting, body aches, headache, fever, and other flu-like symptoms may be noted. Some people who are infected with Cyclospora do not have any symptoms. If not treated, the illness may last from a few days to a month or longer. Symptoms may seem to go away and then return one or more times (relapse).
In 2015, FDA set up a multidisciplinary workgroup to prioritize the development, validation and implementation of a method for detecting Cyclospora in fresh produce. In 2018, FDA began using the newly validated Cyclospora method. The availability of this method is a significant advancement in FDA’s ability to investigate outbreaks of cyclosporiasis and identify the parasite in foods.
At this time, we do not have evidence to suggest that this cluster of illnesses is related to the ongoing Cyclospora outbreak linked to Del Monte vegetable trays.
What is Cyclospora?
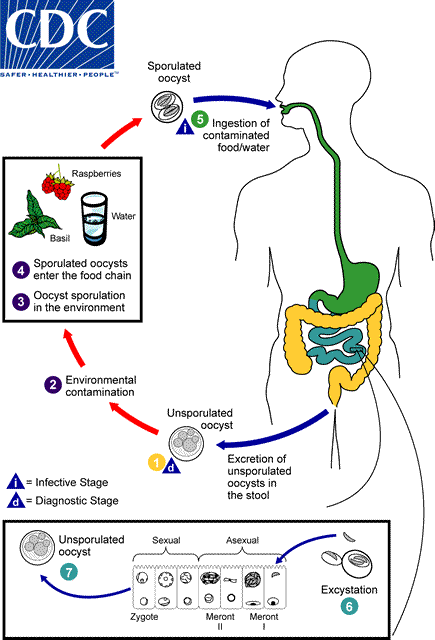
Cyclospora cayetanensis is a microscopic parasite of humans. This parasite, when it contaminates food or water and is then ingested, can cause an intestinal illness called cyclosporiasis.
The Cyclospora parasite needs time (days to weeks) after being passed in a bowel movement to become infectious for another person. Therefore, it is unlikely that cyclosporiasis is passed directly from one person to another.
What are the Symptoms of Cyclosporiasis?
Most people infected with Cyclospora develop diarrhea, with frequent, sometimes explosive, bowel movements. Other common symptoms include loss of appetite, weight loss, stomach cramps/pain, bloating, increased gas, nausea, and fatigue. Vomiting, body aches, headache, fever, and other flu-like symptoms may be noted. Some people who are infected with Cyclospora do not have any symptoms. If not treated, the illness may last from a few days to a month or longer. Symptoms may seem to go away and then return one or more times (relapse).
Who is at Risk?
Anyone who consumed salads from McDonald’s in IA, IL, IN, KY, MN, MO, NE, OH, SD, and WI after May 20, 2018, could have been exposed to the pathogen. People can become infected with Cyclospora by consuming food or water contaminated with the parasite.
Also, at possible risk is anyone who consumed beef, pork and poultry salad and wrap products named in the July 30, 2018, public health alert issued by the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s Food Safety and Inspection Service (FSIS) after May 20, 2018.
What Do Restaurants and Retailers Need To Do?
- Retailers, restaurants, and other food service operators should always practice safe food handling and preparation measures. It is recommended that they wash hands, utensils, and surfaces with hot, soapy water before and after handling food. Wash and sanitize display cases and refrigerators where potentially contaminated products were stored.
- Wash and sanitize cutting boards, surfaces, and utensils used to prepare, serve, or store potentially contaminated products.
- Wash hands with hot water and soap following the cleaning and sanitation process.
- Regular frequent cleaning and sanitizing of food contact surfaces and utensils used in food preparation may help to minimize the likelihood of cross-contamination.
What Do Consumers Need To Do?
Consumers who have symptoms of cyclosporiasis should contact their health care provider to report their symptoms and receive care. Most people infected with Cyclospora develop diarrhea, with frequent, sometimes explosive, bowel movements. Other common symptoms include loss of appetite, weight loss, stomach cramps/pain, bloating, increased gas, nausea, and fatigue. Vomiting, body aches, headache, fever, and other flu-like symptoms (relapse).
Who Should be Contacted?
Contact your healthcare provider if you have diarrhea that lasts for more than three days. The FDA encourages consumers with questions about food safety to Submit An Inquiry, or to visit www.fda.gov/fcic for additional information.

