Archive for the ‘Schistosomiasis’ Category
Interviewing Clarissa Prazeres da Costa, MD about female genital schistosomiasis
Sunday, July 21st, 2019“…..More than 220 million people worldwide suffer from schistosomiasis, and the infection is well known in the global health community. But a subset of infected people – women who carry schisto in their genital organs – get little attention……Female genital schistosomiasis can bring a slew of serious problems including pain, bloody discharges, infertility, incontinence, ulcers, pregnancy problems and tumors…….“
Rakhine, Myanmar: 828 suspected patients and 428 patients diagnosed with schistosomiasis
Tuesday, September 4th, 2018
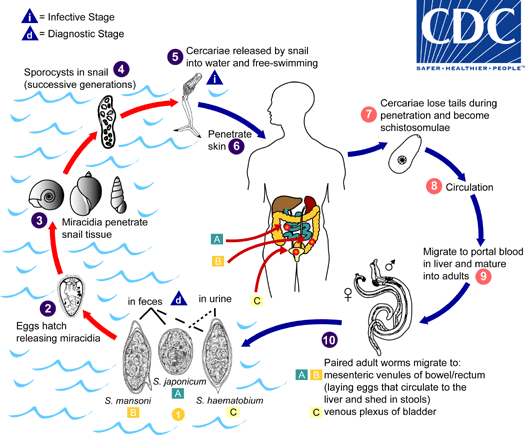
Eggs are eliminated with feces or urine  . Under optimal conditions the eggs hatch and release miracidia
. Under optimal conditions the eggs hatch and release miracidia  , which swim and penetrate specific snail intermediate hosts
, which swim and penetrate specific snail intermediate hosts  . The stages in the snail include 2 generations of sporocysts
. The stages in the snail include 2 generations of sporocysts  and the production of cercariae
and the production of cercariae  . Upon release from the snail, the infective cercariae swim, penetrate the skin of the human host
. Upon release from the snail, the infective cercariae swim, penetrate the skin of the human host  , and shed their forked tail, becoming schistosomulae
, and shed their forked tail, becoming schistosomulae 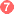 . The schistosomulae migrate through several tissues and stages to their residence in the veins (
. The schistosomulae migrate through several tissues and stages to their residence in the veins ( 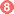 ,
, 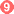 ). Adult worms in humans reside in the mesenteric venules in various locations, which at times seem to be specific for each species
). Adult worms in humans reside in the mesenteric venules in various locations, which at times seem to be specific for each species 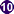 . For instance, S. japonicum is more frequently found in the superior mesenteric veins draining the small intestine
. For instance, S. japonicum is more frequently found in the superior mesenteric veins draining the small intestine  , and S. mansoni occurs more often in the superior mesenteric veins draining the large intestine
, and S. mansoni occurs more often in the superior mesenteric veins draining the large intestine  . However, both species can occupy either location, and they are capable of moving between sites, so it is not possible to state unequivocally that one species only occurs in one location. S. haematobium most often occurs in the venous plexus of bladder
. However, both species can occupy either location, and they are capable of moving between sites, so it is not possible to state unequivocally that one species only occurs in one location. S. haematobium most often occurs in the venous plexus of bladder  , but it can also be found in the rectal venules. The females (size 7 to 20 mm; males slightly smaller) deposit eggs in the small venules of the portal and perivesical systems. The eggs are moved progressively toward the lumen of the intestine (S. mansoni and S. japonicum) and of the bladder and ureters (S. haematobium), and are eliminated with feces or urine, respectively
, but it can also be found in the rectal venules. The females (size 7 to 20 mm; males slightly smaller) deposit eggs in the small venules of the portal and perivesical systems. The eggs are moved progressively toward the lumen of the intestine (S. mansoni and S. japonicum) and of the bladder and ureters (S. haematobium), and are eliminated with feces or urine, respectively  .
.
Pathology of S. mansoni and S. japonicum schistosomiasis includes: Katayama fever, hepatic perisinusoidal egg granulomas, Symmers’ pipe stem periportal fibrosis, portal hypertension, and occasional embolic egg granulomas in brain or spinal cord. Pathology of S. haematobium schistosomiasis includes: hematuria, scarring, calcification, squamous cell carcinoma, and occasional embolic egg granulomas in brain or spinal cord.
Human contact with water is thus necessary for infection by schistosomes. Various animals, such as dogs, cats, rodents, pigs, hourse and goats, serve as reservoirs for S. japonicum, and dogs for S. mekongi.
France: 2 families who had never left Europe have developed schistosomiasis
Friday, August 31st, 2018- Epidemiologists traced the cases to the Cavu River on Corsica.
- Schistosomiasis infects an estimated 230 million people.
- The world’s most widespread parasitic disease after malaria.


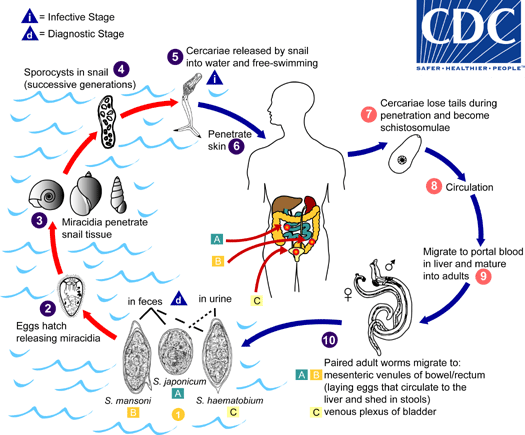
Eggs are eliminated with feces or urine  . Under optimal conditions the eggs hatch and release miracidia
. Under optimal conditions the eggs hatch and release miracidia  , which swim and penetrate specific snail intermediate hosts
, which swim and penetrate specific snail intermediate hosts  . The stages in the snail include 2 generations of sporocysts
. The stages in the snail include 2 generations of sporocysts  and the production of cercariae
and the production of cercariae  . Upon release from the snail, the infective cercariae swim, penetrate the skin of the human host
. Upon release from the snail, the infective cercariae swim, penetrate the skin of the human host  , and shed their forked tail, becoming schistosomulae
, and shed their forked tail, becoming schistosomulae  . The schistosomulae migrate through several tissues and stages to their residence in the veins (
. The schistosomulae migrate through several tissues and stages to their residence in the veins (  ,
,  ). Adult worms in humans reside in the mesenteric venules in various locations, which at times seem to be specific for each species
). Adult worms in humans reside in the mesenteric venules in various locations, which at times seem to be specific for each species  . For instance, S. japonicum is more frequently found in the superior mesenteric veins draining the small intestine
. For instance, S. japonicum is more frequently found in the superior mesenteric veins draining the small intestine  , and S. mansoni occurs more often in the superior mesenteric veins draining the large intestine
, and S. mansoni occurs more often in the superior mesenteric veins draining the large intestine  . However, both species can occupy either location, and they are capable of moving between sites, so it is not possible to state unequivocally that one species only occurs in one location. S. haematobium most often occurs in the venous plexus of bladder
. However, both species can occupy either location, and they are capable of moving between sites, so it is not possible to state unequivocally that one species only occurs in one location. S. haematobium most often occurs in the venous plexus of bladder  , but it can also be found in the rectal venules. The females (size 7 to 20 mm; males slightly smaller) deposit eggs in the small venules of the portal and perivesical systems. The eggs are moved progressively toward the lumen of the intestine (S. mansoni and S. japonicum) and of the bladder and ureters (S. haematobium), and are eliminated with feces or urine, respectively
, but it can also be found in the rectal venules. The females (size 7 to 20 mm; males slightly smaller) deposit eggs in the small venules of the portal and perivesical systems. The eggs are moved progressively toward the lumen of the intestine (S. mansoni and S. japonicum) and of the bladder and ureters (S. haematobium), and are eliminated with feces or urine, respectively  . Pathology of S. mansoni and S. japonicum schistosomiasis includes: Katayama fever, hepatic perisinusoidal egg granulomas, Symmers’ pipe stem periportal fibrosis, portal hypertension, and occasional embolic egg granulomas in brain or spinal cord. Pathology of S. haematobium schistosomiasis includes: hematuria, scarring, calcification, squamous cell carcinoma, and occasional embolic egg granulomas in brain or spinal cord.Human contact with water is thus necessary for infection by schistosomes. Various animals, such as dogs, cats, rodents, pigs, hourse and goats, serve as reservoirs for S. japonicum, and dogs for S. mekongi.
. Pathology of S. mansoni and S. japonicum schistosomiasis includes: Katayama fever, hepatic perisinusoidal egg granulomas, Symmers’ pipe stem periportal fibrosis, portal hypertension, and occasional embolic egg granulomas in brain or spinal cord. Pathology of S. haematobium schistosomiasis includes: hematuria, scarring, calcification, squamous cell carcinoma, and occasional embolic egg granulomas in brain or spinal cord.Human contact with water is thus necessary for infection by schistosomes. Various animals, such as dogs, cats, rodents, pigs, hourse and goats, serve as reservoirs for S. japonicum, and dogs for S. mekongi.
Seventeen volunteers in the Netherlands have agreed to host parasitic worms in their bodies for 12 weeks in order to help advance research toward a vaccine for schistosomiasis
Friday, March 2nd, 2018Six million Egyptians were infected with hepatitis C by unsterile needles during the country’s decades-long fight against schistosomiasis.
Thursday, December 17th, 2015** “…..today, at least 10 percent of Egyptians, nearly nine million people, are chronically infected, the highest rate in the world….
** “….Mr. Ellabbad…was finally cured of hepatitis this spring. An air-conditioning repairman, he took a three-month regimen that included sofosbuvir, first of the new generation of miracle drugs. The pills would have cost more than $84,000 in the United States. He got them free from the Egyptian government, which paid about $900…..”