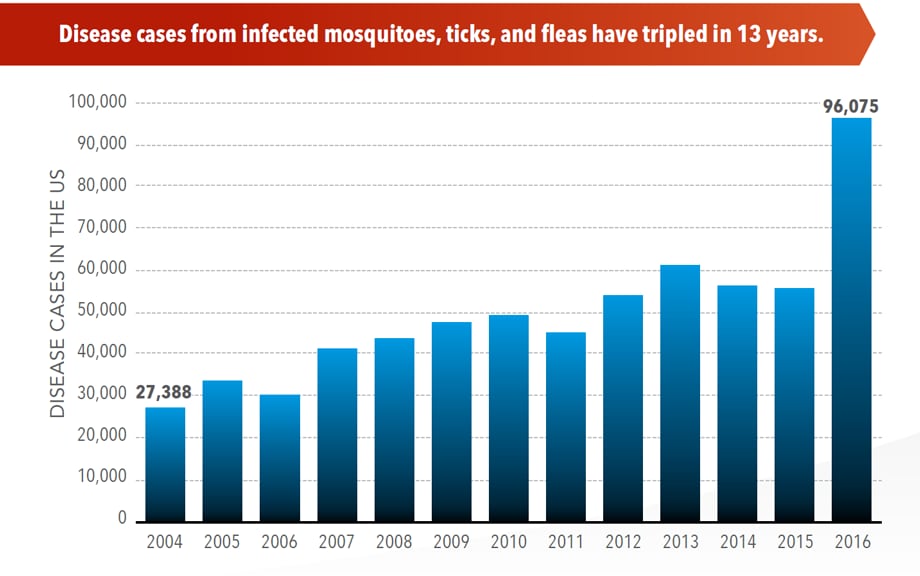
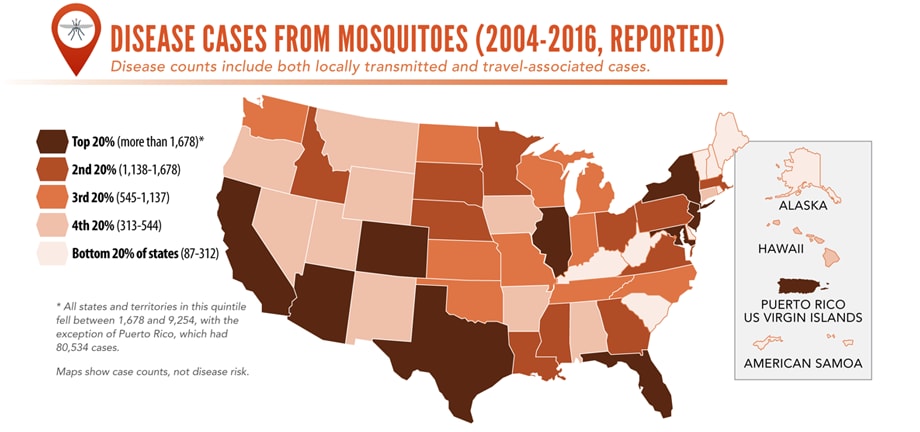
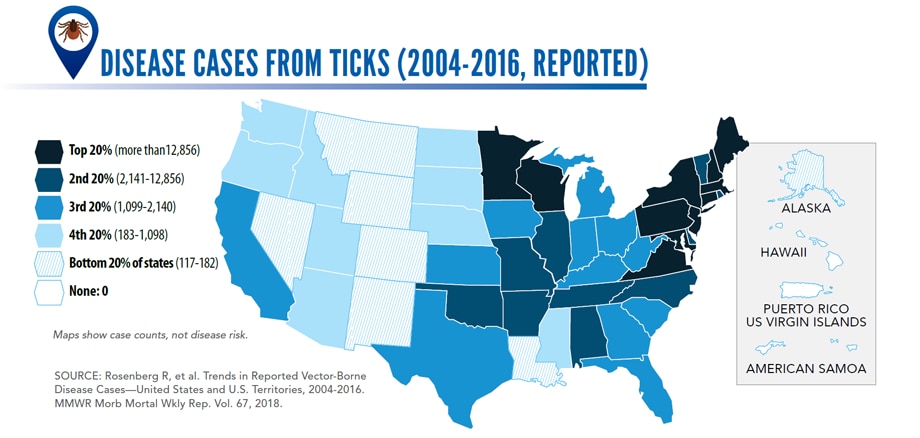
Signs and symptoms
Once contracted, the yellow fever virus incubates in the body for 3 to 6 days. Many people do not experience symptoms, but when these do occur, the most common are fever, muscle pain with prominent backache, headache, loss of appetite, and nausea or vomiting. In most cases, symptoms disappear after 3 to 4 days.
A small percentage of patients, however, enter a second, more toxic phase within 24 hours of recovering from initial symptoms. High fever returns and several body systems are affected, usually the liver and the kidneys. In this phase people are likely to develop jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes, hence the name ‘yellow fever’), dark urine and abdominal pain with vomiting. Bleeding can occur from the mouth, nose, eyes or stomach. Half of the patients who enter the toxic phase die within 7 – 10 days.
Diagnosis
Yellow fever is difficult to diagnose, especially during the early stages. A more severe case can be confused with severe malaria, leptospirosis, viral hepatitis (especially fulminant forms), other haemorrhagic fevers, infection with other flaviviruses (such as dengue haemorrhagic fever), and poisoning.
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing in blood and urine can sometimes detect the virus in early stages of the disease. In later stages, testing to identify antibodies is needed (ELISA and PRNT).
Populations at risk
Forty seven countries in Africa (34) and Central and South America (13) are either endemic for, or have regions that are endemic for, yellow fever. A modelling study based on African data sources estimated the burden of yellow fever during 2013 was 84 000–170 000 severe cases and 29 000–60 000 deaths.
Occasionally travellers who visit yellow fever endemic countries may bring the disease to countries free from yellow fever. In order to prevent such importation of the disease, many countries require proof of vaccination against yellow fever before they will issue a visa, particularly if travellers come from, or have visited yellow fever endemic areas.
In past centuries (17th to 19th), yellow fever was transported to North America and Europe, causing large outbreaks that disrupted economies, development and in some cases decimated populations.
Transmission
The yellow fever virus is an arbovirus of the flavivirus genus and is transmitted by mosquitoes, belonging to the Aedes and Haemogogus species. The different mosquito species live in different habitats – some breed around houses (domestic), others in the jungle (wild), and some in both habitats (semi-domestic). There are 3 types of transmission cycles:
- Sylvatic (or jungle) yellow fever: In tropical rainforests, monkeys, which are the primary reservoir of yellow fever, are bitten by wild mosquitoes of the Aedes and Haemogogus species, which pass the virus on to other monkeys. Occasionally humans working or travelling in the forest are bitten by infected mosquitoes and develop yellow fever.
- Intermediate yellow fever: In this type of transmission, semi-domestic mosquitoes (those that breed both in the wild and around households) infect both monkeys and people. Increased contact between people and infected mosquitoes leads to increased transmission and many separate villages in an area can develop outbreaks at the same time. This is the most common type of outbreak in Africa.
- Urban yellow fever: Large epidemics occur when infected people introduce the virus into heavily populated areas with high density of Aedes aegypti mosquitoes and where most people have little or no immunity, due to lack of vaccination or prior exposure to yellow fever. In these conditions, infected mosquitoes transmit the virus from person to person.
Treatment
Good and early supportive treatment in hospitals improves survival rates. There is currently no specific anti-viral drug for yellow fever but specific care to treat dehydration, liver and kidney failure, and fever improves outcomes. Associated bacterial infections can be treated with antibiotics.
Prevention
1. Vaccination
Vaccination is the most important means of preventing yellow fever.
The yellow fever vaccine is safe, affordable and a single dose provides life-long protection against yellow fever disease. A booster dose of yellow fever vaccine is not needed.
Several vaccination strategies are used to prevent yellow fever disease and transmission: routine infant immunization; mass vaccination campaigns designed to increase coverage in countries at risk; and vaccination of travellers going to yellow fever endemic areas.
In high-risk areas where vaccination coverage is low, prompt recognition and control of outbreaks using mass immunization is critical. It is important to vaccinate most (80% or more) of the population at risk to prevent transmission in a region with a yellow fever outbreak.
There have been rare reports of serious side-effects from the yellow fever vaccine. The rates for these severe ‘adverse events following immunization’ (AEFI), when the vaccine provokes an attack on the liver, the kidneys or on the nervous system are between 0 and 0.21 cases per 10 000 doses in regions where yellow fever is endemic, and from 0.09 to 0.4 cases per 10 000 doses in populations not exposed to the virus (1).
The risk of AEFI is higher for people over 60 years of age and anyone with severe immunodeficiency due to symptomatic HIV/AIDS or other causes, or who have a thymus disorder. People over 60 years of age should be given the vaccine after a careful risk-benefit assessment.
People who are usually excluded from vaccination include:
- infants aged less than 9 months;
- pregnant women – except during a yellow fever outbreak when the risk of infection is high;
- people with severe allergies to egg protein; and
- people with severe immunodeficiency due to symptomatic HIV/AIDS or other causes, or who have a thymus disorder.
In accordance with the International Health Regulations (IHR), countries have the right to require travellers to provide a certificate of yellow fever vaccination. If there are medical grounds for not getting vaccinated, this must be certified by the appropriate authorities. The IHR are a legally binding framework to stop the spread of infectious diseases and other health threats. Requiring the certificate of vaccination from travellers is at the discretion of each State Party, and it is not currently required by all countries.
2. Vector control
The risk of yellow fever transmission in urban areas can be reduced by eliminating potential mosquito breeding sites, including by applying larvicides to water storage containers and other places where standing water collects.
Both vector surveillance and control are components of the prevention and control of vector-borne diseases, especially for transmission control in epidemic situations. For yellow fever, vector surveillance targeting Aedes aegypti and other Aedes species will help inform where there is a risk of an urban outbreak.
Understanding the distribution of these mosquitoes within a country can allow a country to prioritize areas to strengthen their human disease surveillance and testing, and consider vector control activities. There is currently a limited public health arsenal of safe, efficient and cost-effective insecticides that can be used against adult vectors. This is mainly due to the resistance of major vectors to common insecticides and the withdrawal or abandonment of certain pesticides for reasons of safety or the high cost of re-registration.
Historically, mosquito control campaigns successfully eliminated Aedes aegypti, the urban yellow fever vector, from most of Central and South America. However, Aedes aegypti has re-colonized urban areas in the region, raising a renewed risk of urban yellow fever. Mosquito control programmes targeting wild mosquitoes in forested areas are not practical for preventing jungle (or sylvatic) yellow fever transmission.
Personal preventive measures such as clothing minimizing skin exposure and repellents are recommended to avoid mosquito bites. The use of insecticide-treated bed nets is limited by the fact that Aedes mosquitos bite during the daytime.
3. Epidemic preparedness and response
Prompt detection of yellow fever and rapid response through emergency vaccination campaigns are essential for controlling outbreaks. However, underreporting is a concern – the true number of cases is estimated to be 10 to 250 times what is now being reported.
WHO recommends that every at-risk country have at least one national laboratory where basic yellow fever blood tests can be performed. A confirmed case of yellow fever in an unvaccinated population is considered an outbreak. A confirmed case in any context must be fully investigated. Investigation teams must assess and respond to the outbreak with both emergency measures and longer-term immunization plans.
WHO response
In 2016, two linked urban yellow fever outbreaks – in Luanda (Angola) and Kinshasa (Democratic Republic of the Congo), with wider international exportation from Angola to other countries, including China – have shown that yellow fever poses a serious global threat requiring new strategic thinking. The Eliminate Yellow Fever Epidemics (EYE) Strategy was developed to respond to the increased threat of yellow fever urban outbreaks with international spread. Steered by WHO, UNICEF, and Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance, EYE supports 40 countries and involves more than 50 partners.
The global EYE Strategy is guided by three strategic objectives:
- protect at-risk populations
- prevent international spread of yellow fever
- contain outbreaks rapidly.
These objectives are underpinned by five competencies of success:
- affordable vaccines and sustained vaccine market
- strong political commitment at global, regional and country levels
- high-level governance with long-term partnerships
- synergies with other health programmes and sectors
- research and development for better tools and practices.
The EYE strategy is comprehensive, multi-component and multi-partner. In addition to recommending vaccination activities, it calls for building resilient urban centres, planning for urban readiness, and strengthening the application of the International Health Regulations (2005).
The EYE partnership supports yellow fever high and moderate risk countries in Africa and the Americas by strengthening their surveillance and laboratory capacity to respond to yellow fever cases and outbreaks. EYE partners also support the implementation and sustainability of routine immunization programmes and vaccination campaigns (preventive, pre-emptive, reactive) whenever and wherever needed.
To guarantee a rapid and effective response to outbreaks, an emergency stockpile of 6 million doses of yellow fever vaccine, funded by Gavi, is continually replenished. This emergency stockpile is managed by the International Coordinating Group for Vaccine Provision, for which WHO serves as secretariat.
It is expected that by the end of 2026, more than 1 billion people will be protected against yellow fever through vaccination.
(1) WHO. Detection and investigation of serious adverse events following yellow fever vaccination, Geneva, World Health Organization (WHO); 2008.